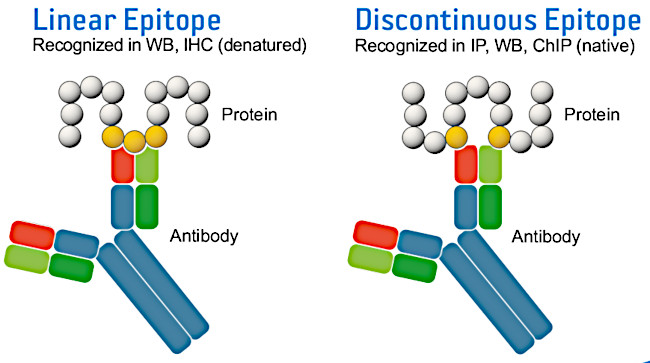
| Immunogen is a substance, for example a protein, peptide, hormone or toxin, which induces an immune response that results in the production of specific antibodies, either polyclonal or monoclonal. In some cases, the term "immunogen" is used interchangeably with the term "antigen", but only an immunogen will elicit a specific immune response. The epitope can be linear or conformational and defines the place where antibody binding occurs. Linear epitopes consist of 2 to 15 amino acids in a subsequent protein sequence. Discontinuous epitopes are amino acids brought together by a protein fold in the three-dimensional protein structure. Unless mapped, the exact amino acid sequence of epitopes recognized by polyclonal antibodies remains unknown. Polyclonal antibodies bind to multiple epitopes on the target protein. Monoclonal antibodies bind to one specific epitope on the target protein. |
 |
